#
# $Id: bivariat.dem,v 1.8 2006/07/06 21:52:19 sfeam Exp $
#
# This demo is very slow and requires unusually large stack size.
# Do not attempt to run this demo under MSDOS.
#
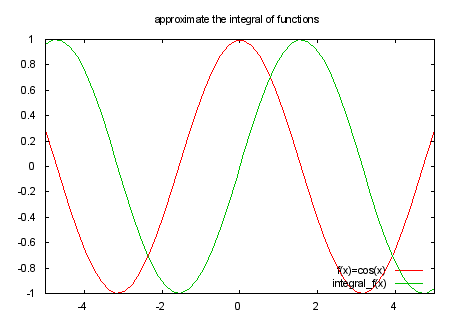
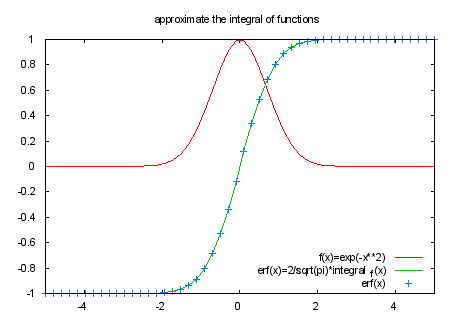
# the function integral_f(x) approximates the integral of f(x) from 0 to x.
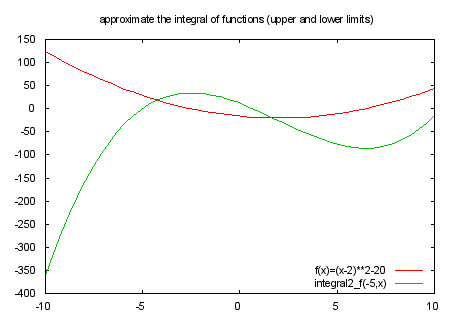
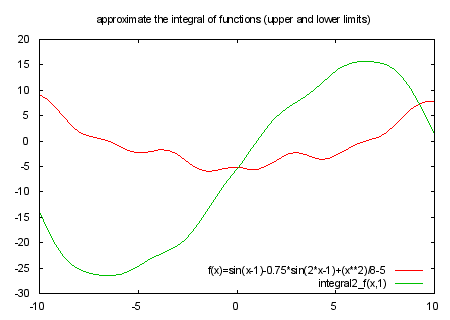
# integral2_f(x,y) approximates the integral from x to y.
# define f(x) to be any single variable function
#
# the integral is calculated using Simpson's rule as
# ( f(x-delta) + 4*f(x-delta/2) + f(x) )*delta/6
# repeated x/delta times (from x down to 0)
#
delta = 0.2
# delta can be set to 0.025 for non-MSDOS machines
#
# integral_f(x) takes one variable, the upper limit. 0 is the lower limit.
# calculate the integral of function f(t) from 0 to x
# choose a step size no larger than delta such that an integral number of
# steps will cover the range of integration.
integral_f(x) = (x>0)?int1a(x,x/ceil(x/delta)):-int1b(x,-x/ceil(-x/delta))
int1a(x,d) = (x<=d*.1) ? 0 : (int1a(x-d,d)+(f(x-d)+4*f(x-d*.5)+f(x))*d/6.)
int1b(x,d) = (x>=-d*.1) ? 0 : (int1b(x+d,d)+(f(x+d)+4*f(x+d*.5)+f(x))*d/6.)
#
# integral2_f(x,y) takes two variables; x is the lower limit, and y the upper.
# calculate the integral of function f(t) from x to y
integral2_f(x,y) = (x<y)?int2(x,y,(y-x)/ceil((y-x)/delta)): \
-int2(y,x,(x-y)/ceil((x-y)/delta))
int2(x,y,d) = (x>y-d*.5) ? 0 : (int2(x+d,y,d) + (f(x)+4*f(x+d*.5)+f(x+d))*d/6.)
set autoscale
set title "approximate the integral of functions"
set samples 50
set key bottom right
f(x) = exp(-x**2)
plot [-5:5] f(x) title "f(x)=exp(-x**2)", \
2/sqrt(pi)*integral_f(x) title "erf(x)=2/sqrt(pi)*integral_f(x)", \
erf(x) with points
Click here for minimal script to generate this plot